The new Tourism Law marks a shift in the direction of Indonesian tourism. Namely, tourism development that is oriented towards sustainability and based on local communities as the main foundation.
This change is crucial to addressing Indonesia's tourism issues, such as equalizing the attractiveness of tourist destinations to tourism marketing.
The new concept of "Tourism Ecosystem" promoted in this Law becomes the main foundation, replacing the old industrial concept, by integrating all supporting components, such as UMKM, to create more inclusive and dispersed tourism. The restructuring of governance through the addition of new articles (4A-C) ensures integrated development planning, more detailed destination arrangements, and modern data-driven and coordinated marketing.
The essence of this change is to place local people and culture as the main pillars (4D), including encouraging community-based tourism and strengthening promotion as an instrument of cultural soft power (4E), as well as recognizing the role of creations and events as tourist attractions (4F).
The modernization of the supporting framework is further strengthened by institutionalizing community participation, strengthening legal aspects, and implementing innovative funding from foreign tourist levies to ensure the financial sustainability of the tourism sector. This modernization also opens up wider involvement of the business world to participate.
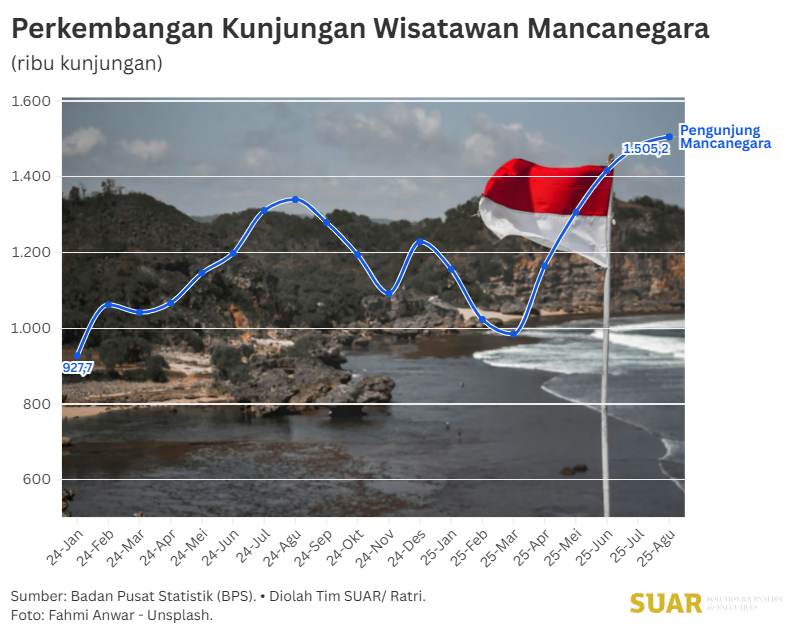
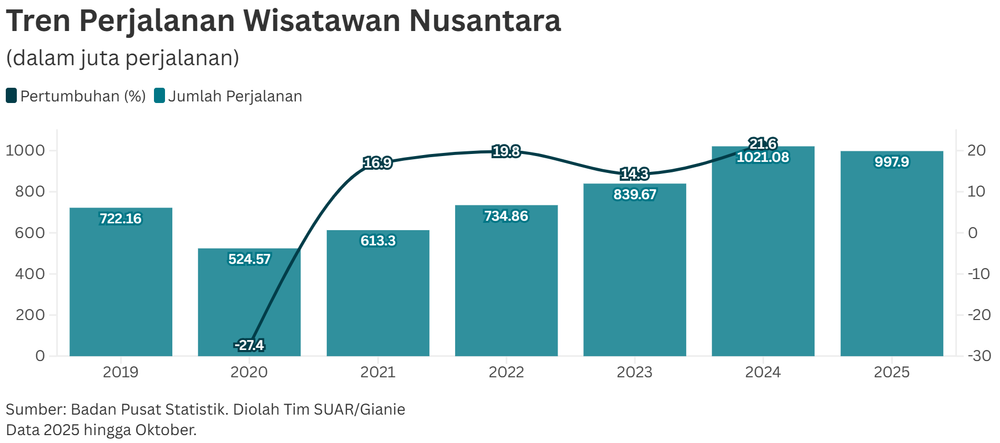
New tourism sector governance is needed to further optimize existing potential even though the annual number of domestic and foreign tourist visitors has shown a positive trend. Data from the Central Bureau of Statistics in the past year showed that the increase in foreign tourist visits reached its peak in August 2025 with 1.505 million visits, up 12.33% compared to August 2024.
Meanwhile, the development of domestic tourist trips also showed strong growth, despite a slight decline to 93.57 million trips in August 2025 from the previous peak in April 2025 (128.58 million). The overall number still recorded a surge of 23.31% compared to August 2024.
Both data indicate that Indonesia's tourism sector, both international and domestic markets, is in a solid growth phase. However, when compared to other Southeast Asian countries, Indonesia ranks 5th with a total visitation of around 7 million visitors.
Thailand took the top spot with the highest number of visits at 16.61 million, far surpassing other countries. Vietnam and Malaysia followed closely, with 10.7 million and 10.1 million visits respectively. Despite showing a positive trend throughout the first half of 2025, tourist arrivals to Indonesia are still far behind other ASEAN countries.
The new Tourism Law is expected to maximize Indonesia's potential. Modern tourism trends do not only make sustainability a supporting aspect, but a principle that must be applied. This law can force destination managers to maintain a balance between economic interests, environmental sustainability, and local culture. Hopefully, this will encourage tourism diversification to new areas, empower local communities, and reduce pressure on classic destinations such as Bali and Jakarta.
The "Tourism Ecosystem" concept introduced aims for holistic integration, ensuring that tourism planning and development is done systematically and involves all stakeholders. Articles supporting the development of tourism villages and kampung wisata, for example, have great potential to spread economic benefits, while at the same time elevating and preserving authentic and unique local cultural wealth, creating new inclusive destinations.