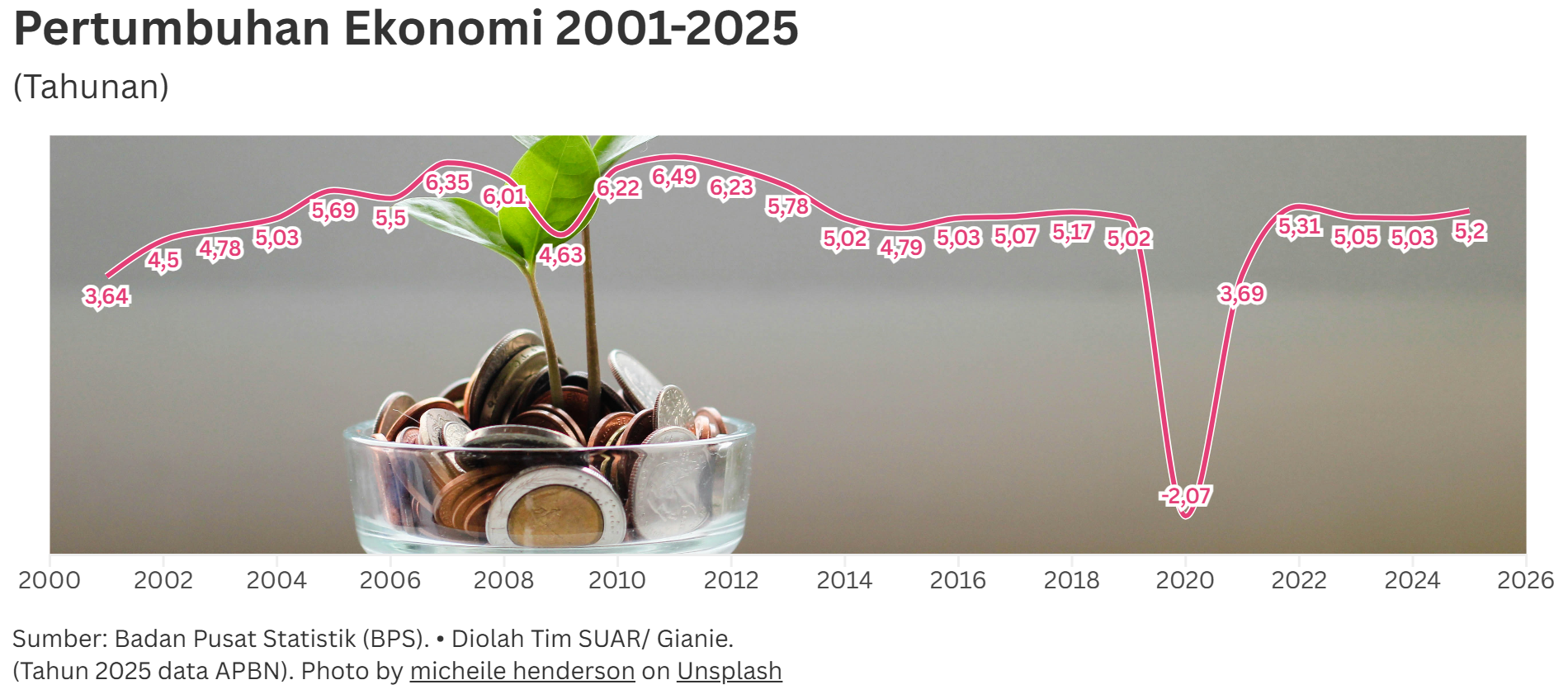
In accordance with the 2025 State Revenue and Expenditure Budget, the government is targeting national economic growth of 5.2% this year. To achieve this target, in the last quarter of 2025, the government must achieve at least 5.8%. With less than a month to go before the end of the year, can this target be achieved?
In the third quarter of 2025, Indonesia's economy grew by 5.04 percent on an annual basis. Cumulatively from the first quarter to the third quarter of 2025, national economic growth reached 5.01 percent. This figure is far from the target of 5.2%. Fiscal, monetary, investment, and public consumption policies must be strengthened to achieve this high target.
Historically, in the period 2001-2024, high economic growth in the fourth quarter exceeded the previous three quarters. This happened not only once, but several times, as shown by data from the Central Statistics Agency.
In 2004, for example, fourth quarter growth was recorded at 7.16%, higher than the previous three quarters which were around 4%, so that cumulative growth in 2004 reached 5.03%. A similar situation occurred in 2006. The same was true for fourth quarter growth in 2009, 2010, 2015, and 2017. However, after the pandemic, fourth quarter economic growth only ranged from 5.01% to 5.04%.
Given this historical context, there is a possibility of high economic growth in the last quarter.
The government is optimistic that economic growth in 2025 will meet its target. This is supported by the expansion of economic activity at the beginning of the fourth quarter of 2025 and the policy strategy for the last quarter of this year.
At the beginning of the fourth quarter, the government, through the Minister of Finance, placed Rp 200 trillion of state funds in state-owned banks with the aim of increasing economic liquidity.
The expected high growth is based on the realization of government spending, economic stimulus packages, and public consumption at the end of the year. The movement of people during the Christmas and New Year holidays is expected to boost national economic growth. To that end, the government is offering discounts or price reductions on transportation tickets ranging from 13-30%.
In addition, social assistance programs worth more than Rp 30 trillion will also boost purchasing power. There is also a mass credit program for housing, which is targeted to be implemented in December 2025. Around 50,000 entrepreneurs will receive people's business credit (KUR) for housing with a ceiling of Rp 5 billion to Rp 20 billion.
However, targets may not be achieved when unexpected events occur. The flash floods and landslides in Aceh, North Sumatra, and West Sumatra that were not handled properly are one example. Disasters that result in food and fuel shortages have the potential to increase inflation. The loss of property suffered by the affected communities will certainly reduce their purchasing power.